Background
The 4D-Modeller package (4DM) is a software tool developed to address a wide range of spatio-temporal problems at various scales, from local to global. It is based on a Bayesian Hierarchical Model (BHM) developed during the Advanced ERC Project GlobalMass (Sha et al., 2019; GlobalMass) that enables the estimation and separation of complex physical processes driving phenomena like sea level rise. The success of the project led to the development of 4DM, applicable to any spatio-temporal process. The package has been successfully applied to diverse problems including COVID-19 transmission, Norwegian hydropower generation, and glacial lake dynamics.
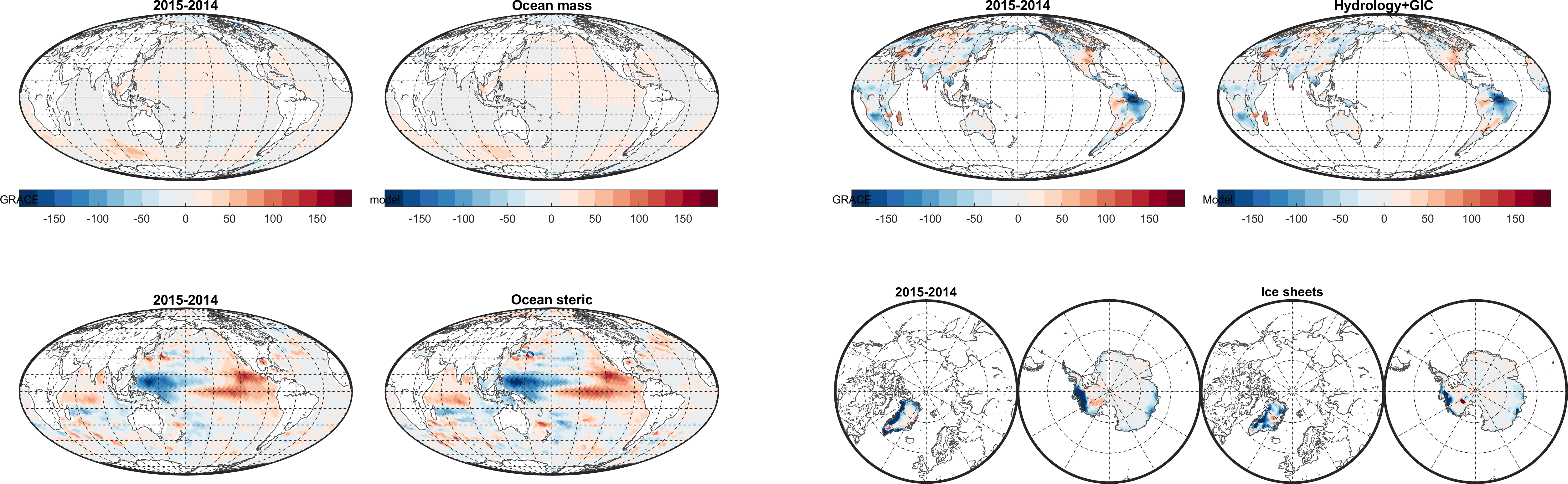
Bayesian Hierarchical Models (BHMs) are powerful tools for understanding complex processes in space and time. They provide probabilistic inference based on observations and can incorporate prior information, constraints, and uncertainties. Traditional Bayesian inference methods face computational challenges with big spatial-temporal data, but recent advancements, such as Integrated Nested Laplace Approximations (INLA) and Stochastic Partial Differential Equations (SPDEs), have improved scalability and computational efficiency. However, utilizing these tools often requires specialized knowledge and statistics expertise.
The goal of 4DM is to simplify the application of BHMs to large-scale problems and reduce the skills burden for users. The package leverages new methods and provides easy-to-understand tutorials that guide users through the modeling process. The tutorials cover the identification of priors, the estimation mesh grid, model inference, and assessment. The development of 4DM follows the Tutorial Driven Software Development practice, which prioritizes scientific questions and involves collaboration between scientists and software developers. This approach ensures robust and user-centric documentation, encouraging wider adoption of the software.
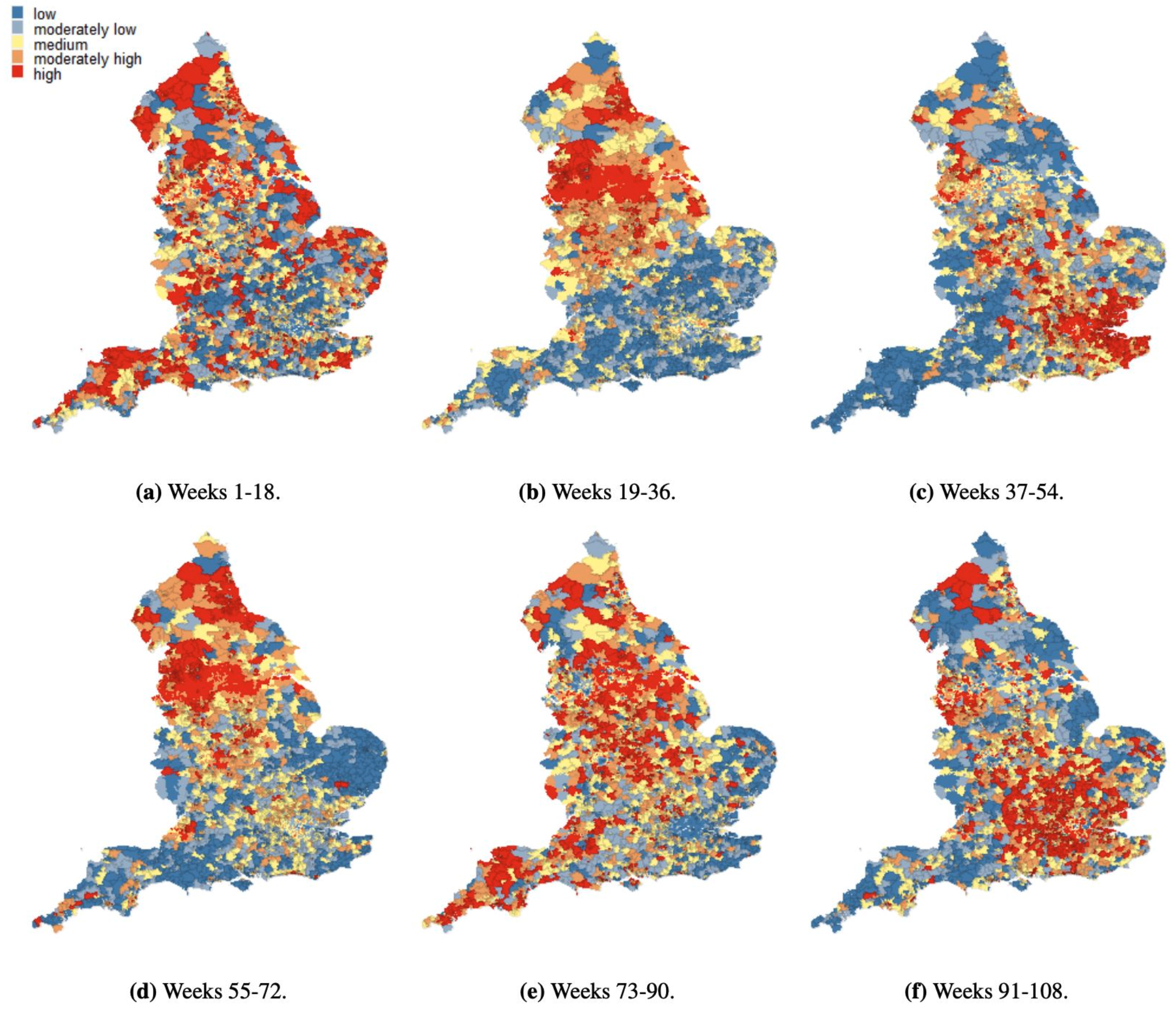
In conclusion, the 4DM package utilizes Bayesian Hierarchical Models and advanced approximation methods to address spatio-temporal problems efficiently. It offers accessible tutorials and documentation to simplify the application of these powerful tools, enabling a broader range of scientists to utilize them in various research fields. Please check the 4DM github